Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2024) |
| Part of a series on the |
| Eastern Orthodox Church |
|---|
| Overview |
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly known simply as the Orthodox Church is a communion composed of up to seventeen separate autocephalous (self-governing) hierarchical churches that profess Eastern Orthodoxy and recognise each other as canonical (regular) Eastern Orthodox Christian churches.[1][2][3][4]
Each constituent church is self-governing;[2] its highest-ranking bishop called the primate (a patriarch, a metropolitan or an archbishop) reports to no higher authority. Each regional church is composed of constituent eparchies (or dioceses) ruled by bishops. Some autocephalous churches have given an eparchy or group of eparchies with varying degrees of autonomy (meaning they have limited self-government). Such autonomous churches maintain varying levels of dependence on their mother church, usually defined in a tomos or another document of autonomy. In many cases, autonomous churches are almost completely self-governing, with the mother church retaining only the right to appoint the highest-ranking bishop (often an archbishop or metropolitan) of the autonomous church.[5]
Normal governance is enacted through a synod of bishops within each church.[6]
Church governance
[edit]The Eastern Orthodox Church is decentralised, having no central authority, earthly head or a single bishop in a leadership role. Thus, the Eastern Orthodox use a synodical system canonically, which is significantly different from the hierarchical organisation of the Catholic Church that follows the doctrine of papal supremacy.[6] References to the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople as a sole authoritative leader are an erroneous interpretation of his title “first among equals".[7][8] His title is of honor rather than authority and in fact the Ecumenical Patriarch has no direct authority over churches other than the Constantinopolitan Church.[9] The Ecumenical Patriarch's unique role is sometimes referred to as being the "spiritual leader" of the Eastern Orthodox Church, although even this is disputed.[10][11]
The autocephalous churches are normally in full communion with each other, so any priest of any of those churches may lawfully minister to any member of any of them, and no member of any is excluded from any form of worship in any of the others, including the reception of the Eucharist. However, there have been varying instances in the history of the Eastern Orthodox Church where communion has been broken between member churches for short periods, particularly over autocephaly issues or disagreements over ecumenism with other Christian denominations.[12][13][14][15]
In early Christian history, the church existed only as a single denomination of five communing churches ruled by five patriarchs: the bishops of Rome, Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, and Jerusalem, collectively referred to as the Pentarchy. Each of the five patriarchs had jurisdiction over bishops in a specified geographic region which did not overlap with the jurisdiction of another patriarch. This continued until 927, when the Bulgarian Patriarchate became the first newly promoted patriarchate to join the original five.[16]
Historically, the Patriarch of Rome was considered to be the "first in place of honor" among the five patriarchs. Disagreement about the limits of his authority was one of the causes of the Great Schism, conventionally dated to the year 1054, which split the previously unified Church into the Roman Catholic Church in the West, headed by the Pope, and the Orthodox Catholic Church (more commonly known today as the Eastern Orthodox Church), led by the four eastern patriarchs. After the schism, the honorary primacy of the Bishop of Rome shifted to the Patriarch of Constantinople, who had previously been accorded second-place rank at the First Council of Constantinople.
In the 5th century, Oriental Orthodoxy separated from Chalcedonian Christianity (and is therefore separate from both the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church), well before the 11th century Great Schism. It should not be confused with Eastern Orthodoxy or Roman Catholicism.
Jurisdictions
[edit]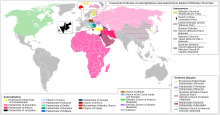
Autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches
[edit]
Ranked in order of seniority, with the year of independence (autocephaly) given in parentheses, where applicable.[17][18] There are a total of 17 autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches which are recognized to various degrees among the communion of the Eastern Orthodox Church.
Canonicity refers to the state of being in communion with the larger Eastern Orthodox Church (making the church in question undisputedly a constituent of the Eastern Orthodox Church), whereas autocephaly refers to the state of being more or less self-governing. Canonicity is binary (two churches are either in communion or not) while autocephaly exists on a spectrum. Disputes over autocephaly often lead to short-term breaks in communion for political reasons. These short-term breaks are typically not due to differences in doctrine or theology.
Four ancient patriarchates
[edit]- Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (independence in AD 330; elevated to the rank of autocephalous Patriarchate in 381; elevated 451 to second see; became first see due to division from the See of Rome in the Great Schism of 1054)
- Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria
- Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch
- Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem (independence in AD 451, elevated to the rank of autocephalous Patriarchate in 451)
The four ancient Eastern Orthodox Patriarchates, along with the See of Rome, formed the historical Pentarchy, and remained in communion with each other after the East-West Schism in 1054. The concept of the Pentarchy and the title of "Patriarch" itself, as opposed to Archbishop or Exarch, is attributed to St Justinian in AD 531.[19]
National patriarchates
[edit]- Bulgarian Orthodox Church (870, Patriarchate since 918/919, recognised by the Patriarchate of Constantinople in 927)[20]
- Georgian Orthodox Church (Patriarchate since 1010)
- Serbian Orthodox Church (1219, Patriarchate since 1346)
- Russian Orthodox Church (1448, recognised in 1589)[21][a]
- Romanian Orthodox Church (1872, recognised in 1885, Patriarchate since 1925)
Autocephalous archbishoprics
[edit]Note:[b]
- Church of Cyprus (recognised in 431)
- Church of Greece (1833, recognised in 1850)[22]
- Albanian Orthodox Church (1922, recognised in 1937)
- Macedonian Orthodox Church (1967, recognised in 2022)
Autocephalous metropolises
[edit]Note:[b]
Universally recognized as canonical, autocephaly disputed
[edit]- Orthodox Church in America (granted by the Russian Orthodox Church in 1970 and recognized by five other churches, but not recognised by the Ecumenical Patriarchate or remaining Churches. Canonicity universally recognized.)[e]
Canonical status undisputed, independence status disputed
[edit]- Ukrainian Orthodox Church (Moscow Patriarchate) (It was given autonomy and independence in 1990 as the Ukrainian Orthodox Church while remaining canonically under the Patriarch of Moscow. It did not follow Metropolitan Filaret Denysenko in forming the Ukrainian Orthodox Church – Kyiv Patriarchate. It declared full independence from the Russian Orthodox Church on 27 May 2022, and was recognised as independent by the Georgian Orthodox Church on 24 March 2023. Its status as an independent church has not been ruled upon by other churches.)[f]
Canonical and autocephalous status disputed
[edit]- Orthodox Church of Ukraine (1992 as Ukrainian Orthodox Church, autocephaly from 15 December 2018, recognised by the Ecumenical Patriarchate on 5 January 2019 and 3 other churches. Its autocephaly and canonicity rejected by remaining Churches, including its rival Ukrainian Churches.)[g]
Canonical and autocephalous status unrecognised
[edit]- A minority of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church – Kyiv Patriarchate led by Filaret (Denysenko) split again in 2019, following internal disputes and concerns as to whether the autocephaly granted by the Ecumenical Patriarchate amounted to true autocephaly due to the conditions imposed. They are not recognized by any church, including its rival Ukrainian Churches.
- The Old Calendarists and True Orthodox split from their local church and are not recognized as canonical, nor do they recognize any of the above churches as canonical. Some maintain communion with the Kyiv Patriarchate under Filaret.
Internal ranking
[edit]The typical order that the four ancient churches appear in the diptychs is the same order given above. While every major church places the four ancient churches in their diptychs before the other autocephalous churches, this order may still differ slightly. For example, in the diptychs of the Russian Orthodox Church and some of its daughter churches (e.g., the Orthodox Church in America), the ranking of the five junior patriarchates is: Russia, Georgia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria. The ranking of the archbishoprics is the same, with the Church of Cyprus being the only ancient one (AD 431).
Autonomous Eastern Orthodox churches
[edit]
- Under the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
- Estonian Apostolic Orthodox Church[α] (autonomy recognised by the Ecumenical Patriarchate but not by the Russian Orthodox Church)
- Orthodox Church of Finland
- Under the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch
- Antiochian Orthodox Christian Archdiocese of North America
- Antiochian Orthodox Archdiocese of São Paulo and All Brazil
- Under the Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem
- Under the Russian Orthodox Church
- Belarusian Orthodox Church
- Metropolis of Chișinău and All Moldova
- Orthodox Church in Japan[α] (autonomy recognised by the Russian Orthodox Church but not by the Ecumenical Patriarchate)
- Chinese Orthodox Church[α] (autonomy recognised by the Russian Orthodox Church but not by the Ecumenical Patriarchate)
- Under the Romanian Orthodox Church
- Metropolis of Bessarabia
- Romanian Orthodox Metropolis of the Americas
- Romanian Orthodox Metropolis of Western and Southern Europe
Semi-autonomous churches
[edit]- Under the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
- Under the Russian Orthodox Church
Limited self-government (not autonomy)
[edit]- Under the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
- Monastic community of Mount Athos
- Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Italy and Malta
- Korean Orthodox Church
- Exarchate of the Philippines
- American Carpatho-Russian Orthodox Diocese
- Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada
- Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the USA
- Under the Russian Orthodox Church
- Under the Romanian Orthodox Church
Unrecognised churches
[edit]

True Orthodox
[edit]True Orthodox Christians are groups of traditionalist Eastern Orthodox churches which have severed communion since the 1920s with the mainstream Eastern Orthodox churches for various reasons, such as calendar reform, the involvement of mainstream Eastern Orthodox in ecumenism, or the refusal to submit to the authority of mainstream Eastern Orthodox Church. The True Orthodox Church in the Soviet Union was also called the Catacomb Church; the True Orthodox in Romania, Bulgaria, Greece and Cyprus are also called Old Calendarists.[25]
These groups refrain from concelebration of the Divine Liturgy with the mainstream Eastern Orthodox, while maintaining that they remain fully within the canonical boundaries of the Church: i.e., professing Eastern Orthodox belief, retaining legitimate apostolic succession, and existing in communities with historical continuity. However, their existence outside of communion with the other churches makes the True Orthodox automatically outside of the Eastern Orthodox Church.
The churches which follow True Orthodoxy are:
- Old Calendarists (numerous groups)
- Serbian True Orthodox Church
- Russian True Orthodox Church (Lazar Zhurbenko)
- Russian Orthodox Autonomous Church
- True Orthodox Metropolis of Germany and Europe[h]
- Macedonian True Orthodox Church
Old Believers
[edit]Old Believers are divided into various churches which recognize neither each other nor the mainstream Eastern Orthodox Church.
Churches that are not recognised despite wanting to
[edit]The following churches recognize all other mainstream Eastern Orthodox churches, but are not recognised by any of them due to various disputes:
- Abkhazian Orthodox Church
- American Orthodox Catholic Church
- Belarusian Autocephalous Orthodox Church
- Latvian Orthodox Church
- Montenegrin Orthodox Church
- Ukrainian Orthodox Church – Kyiv Patriarchate[i]
- Turkish Orthodox Church
Churches that are neither recognised nor fully Eastern Orthodox
[edit]The following churches use the term "Orthodox" in their name and carry belief or the traditions of Eastern Orthodox church, but blend beliefs and traditions from other denominations outside of Eastern Orthodoxy:
- Evangelical Orthodox Church (blends with Protestant Evangelicalism and the Charismatic movement)
- Orthodox-Catholic Church of America (blends with Roman Catholic and Oriental Orthodox elements)
- Nordic Catholic Church in Italy (originally called the Orthodox Church in Italy, it had ties with the UOC-KP; now associates with the Nordic Catholic Church and the Union of Scranton)
- Lusitanian Catholic Orthodox Church (blends with Catholic elements)
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Due to the 2018 Moscow–Constantinople schism, the Russian Orthodox Church has cut ties with the Ecumenical Patriarchate along with several primates of other Churches on this list. The nature of their current relationship is uncertain
- ^ a b In the Orthodox Churches of Greek tradition, the ranks are, from the lowest to the highest, as follows: bishop, metropolitan, archbishop, patriarch. In contrast, in the other Eastern Orthodox Churches, the ranks are, from the lowest to the highest, as follows: bishop, archbishop, metropolitan, patriarch. Thus, an archbishop from an Eastern Orthodox Church of the Greek tradition is equivalent to a metropolitan in the other Eastern Orthodox Churches.
- ^ The primate of the Polish Orthodox Church is referred to as Archbishop of Warsaw and Metropolitan of All Poland, but the Polish Orthodox Church is officially a Metropolis[23]
- ^ The primate of the Czech and Slovak Orthodox Church is referred to as Archbishop of Prešov and Slovakia, Metropolitan of the Czech Lands and Slovakia, but the Czech and Slovak Orthodox Church is officially a Metropolis
- ^ See Orthodox Church in America#Recognition of autocephaly
- ^ As of 27 May 2022, the UOC has formally declared its full autonomy and independence from the Russian Orthodox Church, but did not declare itself autocephalous, while remaining in full communion with the Russian church, as well as with the Orthodox Churches of Antioch, Jerusalem, Serbia, Bulgaria, Romania, Albania, Poland, Czech Lands and Slovakia, and the OCA.[citation needed] However, in 24 March 2023, Georgia has recognised the UOC as an independent church.[24]
- ^ See Orthodox Church of Ukraine#Reactions from Eastern Orthodox churches
- ^ Was previously an Oriental Orthodox archdiocese by the Indian Orthodox Church and later an independent Oriental Orthodox Church; the Church is currently an autonomous True Orthodox Church under the Avlona Synod since 2016
- ^ The UOC-KP merged into the Orthodox Church of Ukraine. However, the UOC-KP was re-established after a conflict between Patriarch Filaret and the primate of the OCU Metropolitan Epiphanius
References
[edit]- ^ "Explainer: The 'Holy And Great Council' Of Orthodox Churches". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
It is -- or should be -- a synod of bishops of all the 14 recognized autocephalous churches of Eastern Orthodox Christianity. Unlike the Catholic Church, which has a single, undisputed leader in the pope, the Orthodox Christians are divided into self-governing provinces, each with its own leadership. The council was meant to be the first meeting of all Orthodox leaders since 787, when the last of the seven ecumenical councils recognized by the heads of both the Eastern and Western Christian Church was held in Nicaea (present-day Iznik in northwestern Turkey).
- ^ a b "Why church conflict in Ukraine reflects historic Russian-Ukrainian tensions". Religion News Service. 2022-02-09. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
Unlike the Catholic Church, which has a single supreme spiritual leader in the pope, the worldwide Orthodox Church is divided into 14 universally recognized, independent, autocephalous or self-headed churches. Each autocephalous church has its own head, or kephale in Greek. Every autocephalous church holds to the same faith as its sister churches. Most autocephalies are national churches, such as the Russian, Romanian and Greek Orthodox churches. Now, the Orthodox Church of Ukraine is claiming its place among the other autocephalous churches.
- ^ "BBC - Religions - Christianity: Eastern Orthodox Church". BBC. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
The nominal head of the Eastern Orthodox Churches is the Patriarch of Constantinople. However, he is only first among equals and has no real authority over Churches other than his own. There are 15 'autocephalous Churches', listed in order of precedence.
- ^ "Patriarchates and Autocephalous Churches". Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ "Autocephalous / Autonomous - Questions & Answers". Orthodox Church in America. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
An "autocephalous" Church is completely self-governing. It elects its own primate and has the right to consecrate its own Holy Chrism, among other prerogatives unique to autocephalous Churches. [The term "autocephalous" literally means "self-heading."] An "autonomous" Church is self-governing to a certain degree in its internal matters, but its head is appointed or confirmed by the autocephalous Church, which nurtures it. An autonomous Church also receives its Holy Chrism from its "Mother Church."
- ^ a b "The Synodal Structure of the Orthodox Church". Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ Clark, Katherine (2009). Orthodox Church - Simple Guides (v3.1 ed.). London: Bravo Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85733-640-5. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ "Autocephaly (6 of 20) - Questions & Answers". Orthodox Church in America. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ "Eastern Orthodoxy". www.britannica.com. Britannica. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ "His All-Holiness Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew". Office of the President. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew, the spiritual leader of 300 million Orthodox Christians worldwide, was elected the 270th archbishop of Constantinople and ecumenical patriarch in October 1991. His tenure has been highlighted by ecumenical and interreligious dialogue — including formal visits with Roman Catholic, Orthodox, other Christian, Jewish and Muslim leaders — as well as efforts to promote religious freedom, human rights and protection of the environment.
- ^ Lourgos, Angie Leventis. "'This made my life complete.' Hundreds greet Orthodox Christian patriarch at South Bend church, part of the spiritual leader's historic visit to the US". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
Bartholomew — the spiritual leader of some 300 million Eastern Orthodox Christians internationally — presided over a service at St. Andrew Greek Orthodox Church in South Bend, Indiana, on Thursday, one of the quieter and more intimate moments during the patriarch's historic 12-day visit to the United States.
- ^ "The Orthodox Schism in the Shadow of Empire". Center for Strategic and International Studies. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ "Ecumenical Council of Florence (1438-1445)". EWTN Global Catholic Television Network. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ "Moscow patriarchate against the union of Rome and Constantinople". AsiaNews.it. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ Burton, Tara Isabella (2018-10-17). "The Eastern Orthodox Churches may split. It's the biggest crisis for these churches in centuries". Vox. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ "The Orthodox Church of Bulgaria". CNEWA. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
In 927 Constantinople recognized the king as Emperor of the Bulgarians and the Archbishop of Preslav as their Patriarch.
- ^ Serbian Orthodox Church official site: Помесне Православне Цркве (Autocephalous Orthodox churches)
- ^ "Orthodox World Churches". Orthodox Church in America. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ "L'idea di pentarchia nella cristianità". homolaicus.com.
- ^ Kiminas, Demetrius (2009-03-01). The Ecumenical Patriarchate. Wildside Press LLC. p. 15. ISBN 978-1-4344-5876-6.
- ^ Kiminas, Demetrius (2009-03-01). The Ecumenical Patriarchate. Wildside Press LLC. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-4344-5876-6.
- ^ "Church of Greece". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2021-03-27.
- ^ "ORTHODOX | METROPOLIA". www.orthodox.pl. Retrieved 2019-01-05.
- ^ "Georgian Patriarch Ilia II addressed the Patriarch of Constantinople in relation to the situation around the UOC". Ukrainian Orthodox Church. 27 March 2023. Retrieved 22 May 2023.
- ^ Parry, Ken; Melling, David J.; Brady, Dimitri; Griffith, Sidney H.; Healey, John F., eds. (2017-09-01) [1999]. The Blackwell Dictionary of Eastern Christianity. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd. pp. 170, 498–9. doi:10.1002/9781405166584. ISBN 978-1-4051-6658-4.
Further reading
[edit]- Territorial Jurisdiction According to Orthodox Canon Law. The Phenomenon of Ethnophyletism in Recent Years, a paper read at the International Congress of Canon Law, 2001 (Ecumenical Patriarchate website)
- World Churches at Orthodox Church in America website
- Religious Organisations - Orthodox Churches at WorldStatesmen.org
- "Independent Orthodox Churches or the Other Orthodox Family of Churches". OCP Pan-Orthodox Network. Archived from the original on 20 October 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)