Coluracetam
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
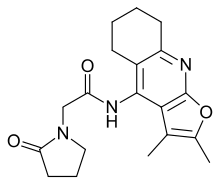
| Formula | C19H23N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 341.411 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Coluracetam (INN; development code BCI-540; formerly MKC-231) is a purported nootropic agent of the racetam family.[1] It contains a chemical group that is a bioisostere of the 9-amino-tetrahydroacridine family. It was initially developed and tested by the Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for Alzheimer's disease. After the drug failed to reach endpoints in its clinical trials it was in-licensed by BrainCells Inc for investigations into major depressive disorder (MDD), which was preceded by being awarded a "Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Program Grant" by the state of California.[2] Findings from phase IIa clinical trials have suggested that it would be a potential medication for comorbid MDD with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).[3] BrainCells Inc is currently[when?] out-licensing the drug for this purpose.[4] It may also have potential use in prevention and treatment of ischemic retinopathy and retinal and optic nerve injury.[medical citation needed]
Coluracetam has been shown to reverse the loss of choline acetyltransferase production in the medial septal nucleus of rats exposed to phencyclidine (PCP), and is considered a potential therapeutic drug for schizophrenia.[5]
Mechanism of action
[edit]Coluracetam enhances high-affinity choline uptake (HACU),[6] which is the rate-limiting step of acetylcholine (ACh) synthesis. Studies have shown coluracetam to improve learning impairment on a single oral dose given to rats which have been exposed to cholinergic neurotoxins. Subsequent studies have shown that it may induce long-lasting procognitive effects in cholinergic neurotoxin-treated rats by changing the choline transporter regulation system.[7]
Legality
[edit]Australia
[edit]Coluracetam is a schedule 4 substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (February 2020).[8] A schedule 4 substance is classified as "Prescription Only Medicine, or Prescription Animal Remedy – Substances, the use or supply of which should be by or on the order of persons permitted by State or Territory legislation to prescribe and should be available from a pharmacist on prescription."[8]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Bessho T, Takashina K, Tabata R, Ohshima C, Chaki H, Yamabe H, et al. (April 1996). "Effect of the novel high affinity choline uptake enhancer 2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-N-(2,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-b] quinolin-4-yl)acetoamide on deficits of water maze learning in rats". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 46 (4): 369–73. PMID 8740080.
- ^ Qualifying Therapeutic Discovery Project Grants for the State of California, IRS.gov.
- ^ BrainCells Inc. Announces Results From Exploratory Phase 2a Trial of BCI-540 Archived 2013-02-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ BCI-540 (coluracetam) | BrainCells Archived 2012-08-31 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Shirayama Y, Yamamoto A, Nishimura T, Katayama S, Kawahara R (September 2007). "Subsequent exposure to the choline uptake enhancer MKC-231 antagonizes phencyclidine-induced behavioral deficits and reduction in septal cholinergic neurons in rats". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 17 (9): 616–26. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.02.011. PMID 17467960. S2CID 22967684.
- ^ Murai S, Saito H, Abe E, Masuda Y, Odashima J, Itoh T (1994). "MKC-231, a choline uptake enhancer, ameliorates working memory deficits and decreased hippocampal acetylcholine induced by ethylcholine aziridinium ion in mice". Journal of Neural Transmission. General Section. 98 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1007/BF01277590. PMID 7710736. S2CID 23321953.
- ^ Bessho T, Takashina K, Eguchi J, Komatsu T, Saito K (July 2008). "MKC-231, a choline-uptake enhancer: (1) long-lasting cognitive improvement after repeated administration in AF64A-treated rats". Journal of Neural Transmission. 115 (7): 1019–25. doi:10.1007/s00702-008-0053-4. PMID 18461272. S2CID 20201642.
- ^ a b Poisons Standard February 2020. comlaw.gov.au
